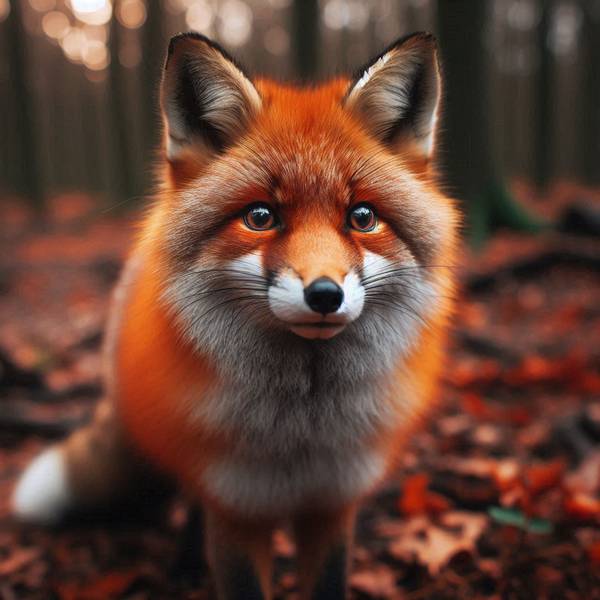
Red Fox (Vulpes vulpes)
The most widespread fox species, known for its adaptability.
• Primary Diet: Small mammals (40-70%)
- Mice, voles, rabbits, and hares
• Secondary Foods:
- Birds and eggs (20-30%)
- Insects and invertebrates (5-20%)
- Fruits and berries (5-30%, seasonal)
- Carrion (varies)
• Urban Areas:
- Human food waste can comprise up to 50% of diet
• Primary Diet: Small mammals (40-70%)
- Mice, voles, rabbits, and hares
• Secondary Foods:
- Birds and eggs (20-30%)
- Insects and invertebrates (5-20%)
- Fruits and berries (5-30%, seasonal)
- Carrion (varies)
• Urban Areas:
- Human food waste can comprise up to 50% of diet
Arctic Fox (Vulpes lagopus)
Adapted to harsh Arctic environments.
• Summer Diet:
- Lemmings and voles (80-90%)
- Birds, eggs, and chicks (10-20%)
- Arctic hare leverets
• Winter Diet:
- Seal carcasses left by polar bears
- Arctic hare
- Fish
- Berries (when available)
• Summer Diet:
- Lemmings and voles (80-90%)
- Birds, eggs, and chicks (10-20%)
- Arctic hare leverets
• Winter Diet:
- Seal carcasses left by polar bears
- Arctic hare
- Fish
- Berries (when available)
Fennec Fox (Vulpes zerda)
Desert-dwelling species with unique dietary adaptations.
• Primary Diet: Insects (40-70%)
- Locusts, beetles, grasshoppers
• Secondary Foods:
- Small mammals (20-30%)
- Birds and eggs (10-15%)
- Fruits and roots (5-10%)
• Water Source: Obtains most water from food
• Primary Diet: Insects (40-70%)
- Locusts, beetles, grasshoppers
• Secondary Foods:
- Small mammals (20-30%)
- Birds and eggs (10-15%)
- Fruits and roots (5-10%)
• Water Source: Obtains most water from food
Gray Fox (Urocyon cinereoargenteus)
Known for its ability to climb trees.
• Omnivorous Diet:
- Small mammals (50-60%)
- Fruits and nuts (20-30%)
- Birds and eggs (10-15%)
- Insects (5-10%)
• Seasonal Variation: More fruits and nuts in autumn
• Omnivorous Diet:
- Small mammals (50-60%)
- Fruits and nuts (20-30%)
- Birds and eggs (10-15%)
- Insects (5-10%)
• Seasonal Variation: More fruits and nuts in autumn
Kit Fox (Vulpes macrotis)
Desert and semi-arid grassland inhabitant.
• Primary Diet: Small mammals (60-80%)
- Kangaroo rats, rabbits
• Secondary Foods:
- Insects (10-20%)
- Birds and reptiles (5-10%)
- Vegetation (minimal)
• Primary Diet: Small mammals (60-80%)
- Kangaroo rats, rabbits
• Secondary Foods:
- Insects (10-20%)
- Birds and reptiles (5-10%)
- Vegetation (minimal)
Swift Fox (Vulpes velox)
Native to North American prairies.
• Primary Diet: Small mammals (60-80%)
- Prairie dogs, ground squirrels
• Secondary Foods:
- Insects (10-25%)
- Birds and eggs (5-10%)
- Carrion (varies)
• Primary Diet: Small mammals (60-80%)
- Prairie dogs, ground squirrels
• Secondary Foods:
- Insects (10-25%)
- Birds and eggs (5-10%)
- Carrion (varies)
Bat-eared Fox (Otocyon megalotis)
African species with unique insectivorous adaptations.
• Primary Diet: Insects (80-90%)
- Termites, beetles, grasshoppers
• Secondary Foods:
- Small mammals (5-10%)
- Fruits and eggs (5-10%)
• Primary Diet: Insects (80-90%)
- Termites, beetles, grasshoppers
• Secondary Foods:
- Small mammals (5-10%)
- Fruits and eggs (5-10%)