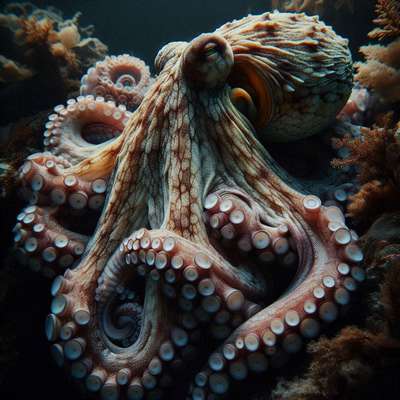
Natural Prey Selection
Octopuses are remarkable marine predators, known for their intelligence and adaptability. Their diet in the wild is diverse, reflecting their opportunistic feeding habits. Studies show that octopuses primarily consume:
1. Crustaceans (40-60% of diet)
2. Mollusks (20-40%)
3. Fish (10-30%)
4. Other invertebrates (5-15%)
The exact composition varies by species and habitat.
Octopuses use several hunting strategies:
• Ambush predation
• Active pursuit
• Probing crevices with arms
Their prey selection is influenced by factors such as:
• Availability of prey species
• Octopus size and age
• Habitat characteristics
• Seasonal variations
1. Crustaceans (40-60% of diet)
2. Mollusks (20-40%)
3. Fish (10-30%)
4. Other invertebrates (5-15%)
The exact composition varies by species and habitat.
Octopuses use several hunting strategies:
• Ambush predation
• Active pursuit
• Probing crevices with arms
Their prey selection is influenced by factors such as:
• Availability of prey species
• Octopus size and age
• Habitat characteristics
• Seasonal variations
Hunting Techniques
Octopuses are remarkable marine predators, employing a diverse array of hunting techniques to capture their prey.
These cephalopods possess 8 arms equipped with over 2,000 suction cups, allowing them to manipulate objects with incredible dexterity.
Octopuses primarily hunt at night, using their keen eyesight and sensitive skin to detect potential meals.
One common technique is the "pounce and grab" method, where an octopus quickly lunges at its target, enveloping it with its arms.
Another strategy involves using their powerful siphon to blow away sand, uncovering hidden prey.
Some species employ a unique "web" technique, spreading their arms to form a canopy-like structure to trap fish.
Octopuses can change color in less than 1 second, using camouflage to ambush unsuspecting victims.
Their intelligence allows them to problem-solve, with some observed using tools like coconut shells for protection while hunting.
An octopus can exert a force of up to 40 pounds with a single arm during capture.
These cephalopods possess 8 arms equipped with over 2,000 suction cups, allowing them to manipulate objects with incredible dexterity.
Octopuses primarily hunt at night, using their keen eyesight and sensitive skin to detect potential meals.
One common technique is the "pounce and grab" method, where an octopus quickly lunges at its target, enveloping it with its arms.
Another strategy involves using their powerful siphon to blow away sand, uncovering hidden prey.
Some species employ a unique "web" technique, spreading their arms to form a canopy-like structure to trap fish.
Octopuses can change color in less than 1 second, using camouflage to ambush unsuspecting victims.
Their intelligence allows them to problem-solve, with some observed using tools like coconut shells for protection while hunting.
An octopus can exert a force of up to 40 pounds with a single arm during capture.
Dietary Adaptations
Octopuses are remarkable marine creatures known for their intelligence and adaptability.
Their dietary habits are equally impressive, showcasing 3 key features:
Versatility:
Octopuses are opportunistic predators, consuming over 200 species of prey.
Hunting techniques:
They employ 4 primary methods:
1. Ambush
2. Pursuit
3. Luring
4. Scavenging.
Tool use: Some species utilize coconut shells and other objects as portable shelters, demonstrating problem-solving skills in foraging.
Octopuses primarily target 5 food groups:
Crustaceans
Mollusks
Fish
Polychaete worms
Echinoderms.
Their diet varies based on 2 factors: habitat and size. Smaller octopuses focus on plankton and small crustaceans, while larger species hunt bigger prey.
Remarkably, octopuses can survive up to 1 month without food by reducing their metabolism by 30%. This adaptation, coupled with their diverse diet, contributes to their success in various marine ecosystems.
Their dietary habits are equally impressive, showcasing 3 key features:
Versatility:
Octopuses are opportunistic predators, consuming over 200 species of prey.
Hunting techniques:
They employ 4 primary methods:
1. Ambush
2. Pursuit
3. Luring
4. Scavenging.
Tool use: Some species utilize coconut shells and other objects as portable shelters, demonstrating problem-solving skills in foraging.
Octopuses primarily target 5 food groups:
Crustaceans
Mollusks
Fish
Polychaete worms
Echinoderms.
Their diet varies based on 2 factors: habitat and size. Smaller octopuses focus on plankton and small crustaceans, while larger species hunt bigger prey.
Remarkably, octopuses can survive up to 1 month without food by reducing their metabolism by 30%. This adaptation, coupled with their diverse diet, contributes to their success in various marine ecosystems.